From the Medieval Research Blog: "St. Augustine: Florida’s Medieval City"
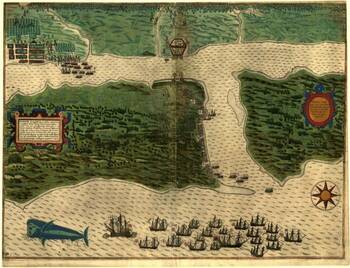
Along oyster beds, sand dunes, and marshy coastal lowlands rise the church spires and walls of a medieval coastal city. This isn’t Northumbria’s Holy Island or Normandy’s Mont-St-Michel, though. This is the City of St. Augustine, Florida, the oldest city continuously occupied by Europeans and African-Americans in North America. This settlement on Florida’s First Coast predates the arrival of the Mayflower pilgrims at Plymouth in 1620 and even the 1607 founding of Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement.
The Age of Reconnaissance
St. Augustine was founded by the Spanish in 1565 as part of the fifteenth- and sixteenth-century European push to discover, explore, and settle new lands beyond Europe. This “Age of Reconnaissance” is one of the hallmarks for historians of the transition from the late Middle Ages into the Early Modern period in Europe.
Historian J. H. Parry describes the medieval beginnings of this push, especially in Spain:
“The initial steps in expansion were modest indeed: the rash seizure by a Portuguese force of a fortress in Morocco; the tentative extension of fishing and, a little later, trading, along the Atlantic coast of North Africa; the prosaic settlement by vine and sugar cultivators, by log-cutters and sheep-farmers, of certain islands in the eastern Atlantic. There was little, in these early- and mid-fifteenth-century ventures, to suggest world-wide expansion.”
In the later fifteenth-century, though, this expansion indeed exploded globally. The desire to expand wealth through acquisition of new lands, slave labor, and precious metals and stones, as well as the desire to convert any newly-discovered peoples to Catholicism, were powerful enticements for Spain to explore. Developments in nautical navigation, map-making, and ship technology made exploration possible.
Spain’s first encounter with the Florida coast came during the explorations of a medieval Spaniard, Juan Ponce de Léon (b. ca. 1460 in Léon, Spain). In early April 1513, with a license from Spain’s King Ferdinand II (1452–1516), Ponce de Léon sailed from Puerto Rico looking for Bimini (the Bahamas) and, legend has it, the Fountain of Youth. He found Florida instead, landing somewhere between St. Augustine and Melbourne Beach.
Claiming it for Spain, he gave the supposed island its Spanish name of La Florida, or Pascua Florida, depending on which source you look at; both names suggest Ponce de Léon was struck by the abundance of flowers he must have seen. (“Pascua Florida Day” is a state holiday and is celebrated on or around April 2nd each year.) He then sailed southward around the peninsula to explore further. Ponce de Léon returned to Spain and procured Spain’s consent to colonize the New World; thus Spanish settlement began.
This is an excerpt from "St. Augustine: Florida’s Medieval City (Part I)" written by Megan J. Hall (Ph.D '16). Read the full story (and check out Part II as well!)
Originally published by at medieval.nd.edu on September 19, 2022.
Latest Research
- Visit by Fr. Paolo Benanti, AI advisor to Pope Francis, deepens Notre Dame’s commitment to socially responsible data and AI innovationBest known for providing expert advice on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to Pope Francis, Fr. Paolo Benanti has a contagious enthusiasm for the ethics of technological advancement.…
- Subhash L. Shinde elected 2024 MRS Fellow…
- Notre Dame launches University-wide Democracy Initiative to advance research, education and policy efforts to sustain and enhance democracyThe University of Notre Dame has launched an ambitious new Democracy Initiative, an interdisciplinary research, education and policy effort focused on advancing solutions to sustain and strengthen global democracy.…
- Researchers update supercomputing infrastructure that powers research at Notre DameTwice each year, the High Performance Computing (HPC) team at the Center for Research Computing (CRC), and a ten-person team work 150–200 hours to ensure that Notre Dame’s research computing…
- Notre Dame researcher explores how technology can defend democracyGrowing public disenchantment with social media often highlights how it has poisoned political discourse. Critics say its business model leverages negative emotions to maximize user engagement, fueling mistrust and polarization. Keough School of Global Affairs scholar Lisa Schirch sees opportunity in a new class of deliberative technologies and their implications for democracy.
- Notre Dame International extends global outreach and presence with new name: Notre Dame GlobalBeginning today (April 15), Notre Dame International will adopt a new name, Notre Dame Global, and will introduce itself on its new portal at global.nd.edu. The rebrand emphasizes the interconnectedness of the University of Notre Dame’s 12 locations around the world and reflects Notre Dame Global’s vital role in advancing Notre Dame as a leading global Catholic research university, on par with but distinct from the world’s best private universities.













