NDTL Develops CO₂ Component Test Capability and Successfully Tests High Efficiency Transcritical CO₂ Compressor
NDTL Propulsion and Power (NDTL) has designed and built a closed test loop and a CO₂ storage and management system to support testing for supercritical and transcritical CO₂ power and thermal management components. The test loop can be installed in NDTL’s 10-megawatt, 5-megawatt, or 3-megawatt test cells to match the power, speed, and flow requirements of a particular test article. NDTL recently completed testing of the first stage of a high-efficiency multistage transcritical CO₂ compressor.
The development of high-efficiency compression systems is important for the design of CO₂-based power and heat pump cycles. Axial compressors inherently have higher efficiency compared to centrifugal and reciprocating machines, but they have not yet been tested or demonstrated using CO₂ as the working fluid. The high fluid density, high power density, and significant real gas effects present technical challenges in designing and testing an axial compressor.
With support from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), the team composed of NDTL, Echogen, and the University of Cincinnati is demonstrating the system efficiency advantages of utilizing axial compressors in renewable energy storage systems. This is being accomplished with the design and test of a 3-stage transcritical CO₂ axial compressor.
NDTL designed and fabricated the test loop, performed the mechanical design of the high-power density compressor, and is executing the test program. The University of Cincinnati, employing best practices from air-breathing compressors for aero-propulsion engines, performed the aerodynamic compressor design. Echogen leads the overall program and developed the transition path to a fielded system. Echogen has also provided its expertise in supercritical CO₂ systems.
The test loop consists of a variable speed drive motor, CO₂ inventory system, a heat exchanger between the CO₂ loop and the water/glycol loop, high accuracy Coriolis flowmeter, and cooling towers. The closed loop is installed in a test cell fully equipped with data acquisition and control systems.

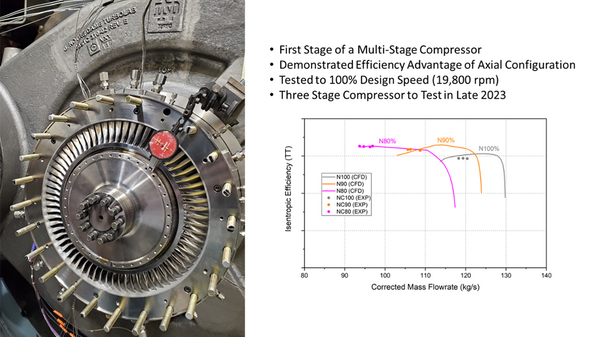
The initial testing of the first stage of the 3-stage axial compressor was completed at NDTL using the closed sCO₂ compressor test loop installed in the 10 MW cell. Steady-state conditions were obtained by removing enthalpy from the loop using a CO₂ – water/glycol heat exchanger. The nominal design speed, pressure ratio, and mass flow rate of the compressor are 19,800 rpm, 1.42, and 125 kg/s, respectively.
The compressor mapping test was performed from 60% to 100% corrected speed. The pressure ratio and the efficiency of the compressor were measured through the total pressure and total temperature rakes, which were installed at the inlet and the exit of the test compressor. All nine rakes were calibrated via an in-house flow calibration jet facility. The measured pressure ratio and the efficiency of the compressor aligned well with design predictions, and the measured isentropic efficiency of the compressor was above 90%.
NDTL is preparing to begin testing of the 3-stage compressor. Updates are forthcoming.
Originally published by at ndtl.nd.edu on November 27, 2023.
Latest Research
- Fighting for maternal healthThe United States has the highest maternal mortality rate of developed nations. An innovative postpartum care model from Notre Dame can save mothers around the globe. Read the story Originally…
- NSF Cyber SMART’s fall meeting shapes fifth year of project, legacy and future plans, and adds new memberThe U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Cyber SMART center gathered for its fall meeting on the University of Notre Dame campus this September. The meeting served as a checkpoint with progress reports and new projects from research leads and students…
- Slavic and Eurasian studies professor wins Humboldt fellowship to research how Russia’s religious past shapes its presentWhen Russia invaded Ukraine on Feb. 24, 2022, Sean Griffin realized his second book needed a new title. Griffin, an associate professor in the University of Notre Dame’s Department of…
- Notre Dame’s R.I.S.E. AI Conference builds interdisciplinary collaboration to inform human-centered artificial intelligenceAs artificial intelligence (AI) transforms nearly every sector of society — from healthcare and education to governance and global development — a critical question emerges: How can we conscientiously design and deploy these powerful technologies to positively impact society? This…
- University of Notre Dame joins the Global Coalition of Ukrainian StudiesThe University of Notre Dame has joined the Global Coalition of Ukrainian Studies after signing a Memorandum of Cooperation (MOC), formalized on September 24, 2025, at the Ukrainian Institute of America in New York City. Notre Dame joined four other American…
- The University of Notre Dame’s Mendoza College of Business and Industry Labs team up to inspire national security manufacturing competitiveness in the regionThe South Bend - Elkhart Region is full of manufacturing companies that are poised to grow, and Executive Master of Business Administration (EMBA) and Master of Business Administration (MBA) students at the University of Notre Dame are finding innovative ways to contribute to that growth. Earlier…













