Using forest resources strengthens food security, study finds
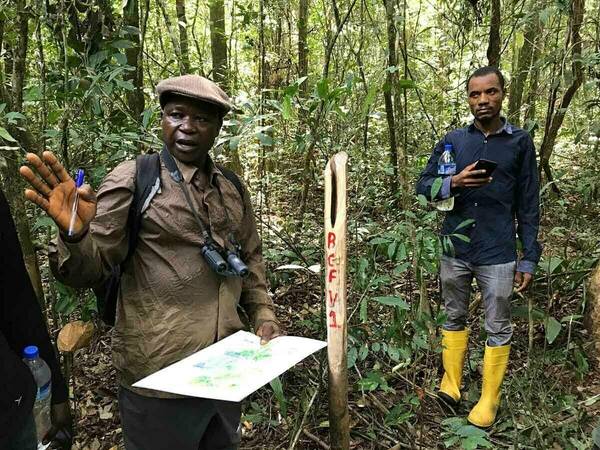

Forests can reduce hunger in rural households while also capturing carbon and advancing sustainability goals for low- and middle-income countries, according to new research by University of Notre Dame experts.
Households in Liberia that participated in forest-based activities — including collecting and processing timber, hunting bushmeat or gathering edible plants — reduced their food scarcity by 84 percent, according to a study published in the journal Food Security. The research was conducted by Daniel C. Miller, associate professor of environmental policy at Notre Dame’s Keough School of Global Affairs, and co-author Festus Amadu, a former Notre Dame postdoctoral researcher who is now assistant professor of climate policy at Florida Gulf Coast University.
“Previous research has shown that forests benefit people, but now we have evidence on a national scale,” Miller said. “Forests are a vital source of food security for forest-adjacent households in Liberia, the most forested country in West Africa.”
Miller and Amadu analyzed data from a 2019 survey by the Liberian government and the World Bank. Miller, a former World Bank senior forestry specialist, helped design the survey, which collected data from nearly 3,000 households living near forests across all 15 counties in Liberia. The researchers found that when households reported engaging in forest-based activities, they also reported food insecurity for almost three fewer months out of the year.
Food insecurity is severe in many countries in sub-Saharan Africa, including Liberia, where most rural households do not have access to enough food to meet their daily calorie intake requirements for the whole year, Miller said. Causes of this food insecurity include extreme weather events, political instability, and poor agricultural productivity caused by natural resource depletion. Existing research shows that forests may be more resilient to some of these stresses, making them increasingly vital for reducing food insecurity in countries such as Liberia, where forests comprise 69 percent of its land area.
“Forests do a lot of things for us as human beings, and yet their manifold contributions are not systematically studied and documented,” Miller said. “While forests will never substitute for agriculture on any large scale, they can serve as an important food source, particularly in lean times.”
Miller said the study’s methodology — using forest-specific data acquired on a national scale — could be applied to other forest-rich, economically poor countries in West Africa and elsewhere to further understand how forests can mitigate food insecurity.
“Forests can and should be considered by national governments in other countries not only for their climate and environmental benefits, but for their potential to support human development and well-being,” he said.
The research was supported by the Forests & Livelihoods: Assessment, Research and Engagement (FLARE) network, which Miller leads, with funding from Notre Dame Research, the Notre Dame Environmental Change Initiative and the Keough School.
In future studies, Miller and Amadu will examine how forest governance, particularly at the community level, affects how people living near forests can benefit from them. Miller also said the study’s findings have important policy implications and could be used by policymakers focused on forest management and conservation.
“The benefits that forests create for the citizens of a country are yet another reason why forests are worth managing well and conserving,” Miller said. “When you have empirical evidence at the national level, it becomes relevant not only in scholarship but also for the policy realm.”
Originally published by Renée LaReau at keough.nd.edu on July 22.
Contact: Tracy DeStazio, associate director of media relations, 574-631-9958 or tdestazi@nd.edu
Latest Colleges & Schools
- Faculty receive prestigious early career awards from National Science FoundationDuring the 2024-25 academic year, four researchers in the University of Notre Dame’s Colleges of Engineering and Science received early-career awards from the National Science Foundation.
- ‘Prebunking’ false election claims may boost trust in electionsIn recent years, democracies worldwide have seen a growing erosion of trust in election outcomes and institutions, driven in part by fears of widespread fraud. New Notre Dame research finds that “prebunking” — providing accurate information before false claims spread — boosts trust in elections more effectively than traditional fact-checking.
- Justice Amy Coney Barrett to deliver Center for Citizenship and Constitutional Government lectureAmy Coney Barrett, associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, will speak at the University of Notre Dame at 4 p.m. Sept. 12 in the Leighton Concert Hall of the DeBartolo Performing Arts Center.
- Three Notre Dame researchers win NEH grants for humanities-based projectsDavid Hernandez, the Eli J. and Helen Shaheen Associate Professor of Classics, and Morgan Munsen, senior research and partnerships program manager at the Nanovic Institute for European Studies in the Keough School of Global Affairs, have each won an NEH Collaborative Research grant. Thomas A. Stapleford, associate professor in the Program of Liberal Studies, is leading a team that has been awarded a Humanities Research Center on Artificial Intelligence grant.
- Open-access database offers insights into U.S. congressional candidatesEach election cycle, thousands of candidates vie for seats in the U.S. House of Representatives and the Senate. Until now, there has been no comprehensive, publicly available resource cataloging what those candidates say about who they are or what they stand for. A new open-access database called CampaignView, created by researchers at the University of Notre Dame, offers researchers, journalists and educators a powerful tool to understand congressional elections.
- First impressions count: How babies are talked about during ultrasounds impacts parent perceptions, caregiving relationshipPsychologist Kaylin Hill studied the impact of a parent’s first impression of their baby during an ultrasound exam. The words used by the medical professional to describe the baby (positive or negative) influence how the parents perceive their baby, relate to them after they're born and even how that child behaves as a toddler. The research has broad implications for how we train medical professionals to interact with expectant parents, as well as how we care for parents during the perinatal period when they are most susceptible to depression.